Listen to the article – Defense Industry’s Strategic Outlook – SWOT Analysis
The world is witnessing a global militarization. This surge, fueled by escalating geopolitical tensions, conflicts and technological advancements, led nations to reevaluate their national priorities and place emphasis on bolstering their defense capabilities.
Moreover, the rising military expenditures are evident around the world, particularly in the three current geopolitical hotspots being Eastern Europe, Middle East, and the Indo-Pacific. Despite the current wars in Ukraine and Gaza Strip, current military build-up around Yemen, and a potential conflict with Iran are indicating that these events could transform into a regional war and make the world more belligerent. Despite such unwelcome news, economic challenges and natural disasters, the global defense market continues to evolve, driven by this chain of events.
Against this background, the defense industry serves as a cornerstone in the preservation of national security interests worldwide. Within this critical sector, this SWOT analysis offers a strategic framework to assess strengths and weaknesses, along with opportunities and threats.
SWOT Analysis
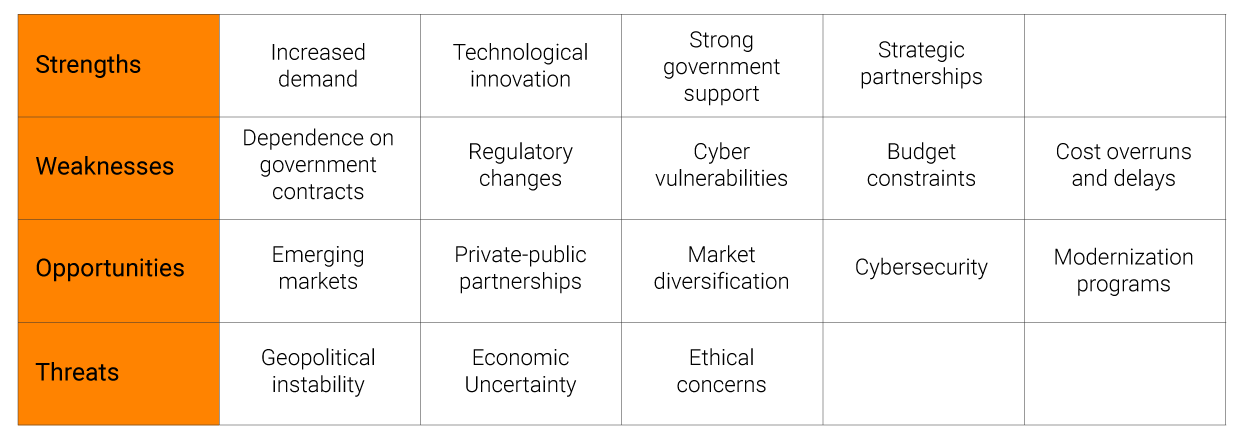
This analysis scrutinizes the defense industry’s landscape, highlighting strengths such as meeting increased demand, driving technological innovation, securing strong government support, and fostering strategic partnerships. Concurrently, it addresses weaknesses stemming from reliance on government contracts, exposure to regulatory changes, cyber vulnerabilities, budgetary constraints, as well as operational cost overruns and delays. Furthermore, it explores opportunities in emerging markets, collaborative ventures between the private and the public sector, market diversification, cybersecurity issues and modernization efforts, while acknowledging threats posed by geopolitical instability, economic fluctuations, and ethical considerations. Through this comprehensive examination, stakeholders can chart a course towards informed decision-making to propel sustainable advancement in this vital domain. As the guardians of security and stability, the defense industry must vigilantly assess its strategic position to ensure its readiness to meet the challenges and opportunities of tomorrow.
01
Strengths
01
Strengths
The defense industry exhibits formidable strengths, including increased demand, continuous technological advancements fostering innovation, strong governmental support, and strategic collaborations with various entities.
- Increased demand
Increased demand for defense products and services globally and locally is set to rise, reflecting a growing market for international defense exports driven by geopolitical tensions and security challenges.
International defense exports represent lucrative avenues for revenue generation and market expansion, prompting defense companies to actively promote their products and services to foreign governments and defense organizations, thereby establishing long-term relationships and enhancing global reputation. Triggered by geopolitical tensions, particularly in response to the conflicts in Ukraine, Gaza Strip, and more recently the events in the Red Sea and Yemen, led to increased demand of a vast range of defense products boosting market expansion.
Notably, South Korea’s defense exports surged to approximately USD 14 billion in 2023, solidifying its position among the world’s top ten defense exporters for the second consecutive year, driven by strategic initiatives aimed at expanding export markets and diversifying product offerings. Similarly, US defense companies experienced a remarkable surge in international defense exports in 2023, totaling USD 81 billion.[1] The UAE’s defense industry has also experienced significant growth, particularly in the development of missiles and munitions, with key players such as Halcon, ADASI, and Al Tariq leading advancements in precision-guided munitions and weaponry. Furthermore, collaborations such as the memorandum of understanding between South Korea and Saudi Arabia highlight the potential for robust defense cooperation, with a focus on joint development projects and tapping into the growing demand for weapons in the Middle East. Therefore, international defense exports are highly profitable opportunities for defense companies, driving them to actively market their offerings to foreign governments and defense entities. This initiative-taking approach not only boosts revenue but also facilitates market expansion, long-term partnerships, and the enhancement of global standing within the defense industry.
The increased demand is also visible in local terms as well. A glance at the US defense contracting landscape for 2024 reveals a substantial potential for industry growth and advancement. These opportunities, valued at USD 61.9 billion, encompass a diverse array of sectors including construction, information technology, airlift services, maintenance, cybersecurity, strategic support, missile defense, and technology development.[2] By capitalizing on these avenues, the defense industry can bolster its position in the market, mitigate risks associated with dependency on foreign markets, and contribute to national security objectives. Leveraging this trend effectively will likely enable defense contractors to expand their market presence, enhance technological capabilities, and forge strategic partnerships with government agencies. Therefore, the increased demand locally is another potential avenue for growth amid rising geopolitical tensions and challenges, and is also highlighting the potential for innovation, collaboration, and sustained growth in the coming fiscal year.
How can we help?
Intelligence Solutions
The combination of business, market and strategic intelligence ensures result-driven outcomes for our customers.
Defense and security solutions
Our holistic business approach to the defense and security industry delivers creative solutions tailored to benefit the defense industry stakeholders.
Risk management
Risk management through the responsibility of taking risk ownership while ensuring safety and security
In conclusion, geopolitical tensions and security challenges are driving the increased demand up for defense products locally as well as internationally, providing avenues for innovation, collaboration, market expansion, partnerships, and sustainable growth.
- Technological innovation
Technological innovation is a strength for defense companies allowing the development and commercialization of cutting-edge solutions, maintaining competitiveness and relevance in the market. The defense industry’s reputation for pioneering technological innovation stems from its robust investment in R&D, development of advanced weapon systems, cultivation of cybersecurity expertise, and fostering of collaborative innovation ecosystems.
Investment in R&D is a keystone of the defense industry that is fueling technological innovation, where technological superiority translates to military effectiveness and national security. Last year, the Pentagon introduced its most substantial innovation and modernization budget yet, seeking USD 145 billion from US Congress for fiscal year 2024.[3]
This budget aims to enhance critical technology programs and forge stronger partnerships with industry. Notable allocations include USD 1.4 billion for the Joint All-Domain Command and Control initiative, aimed at seamlessly connecting military forces across different domains. Additionally, USD 687 million will support the Rapid Defense Experimentation Reserve, focusing on addressing high-priority capability gaps using advanced technology. Examples from recent data highlight the diverse allocation of R&D funds within the US DoD encompassing initiatives ranging from basic research to the development of specific weapon systems. In its effort to maintain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic defense landscape, the US DoD has unveiled several significant contract opportunities aimed at bolstering future defense operations, including initiatives targeting space and missile defense capabilities, avionics system security, and next-generation microelectronics manufacturing.[4]
The current US administration’s 2024 budget request, totaling USD 145.0 billion for R&D program elements, underscores the ongoing commitment to advancing defense capabilities through technological advancements. Despite proposed cuts in certain areas, the importance of R&D investments in fostering technological innovation and sustaining military readiness remains paramount. Therefore, by allocating resources toward investing in R&D, defense companies are driving technological advancements to maintain military superiority and contribute to broader technological innovations.

Development of advanced weapon systems represents a pinnacle of military capability, deterrence and strategic advantage. The Ukraine conflict serves as a prime example where technological advancements became a game-changer of warfare.[5] In addition, the new US National Defense Industrial Strategy emphasizes that the development and deployment of advanced weapon systems have become increasingly vital to maintaining strategic advantage and safeguarding national interests.[6] Moreover, faced with the increasing threat of peer competitors’ advanced weapon systems, allies are focusing on developing hypersonic weapon systems, so-called glide vehicle and cruise missiles to address this trend. Hence, developing advanced weapon systems provides boosting of military capabilities, deterrence, and also enables strategic advantage over peer competitors.
Cybersecurity expertise positively influences the development of resilient defense systems. Such expertise will boost the protection of critical information assets, adaptation to evolving cyber threats, collaboration across stakeholders and adherence to cybersecurity standards. As cyber threats continue to escalate in frequency, sophistication, and impact, the need for robust cybersecurity measures has become paramount in the defense industry. Effective cybersecurity expertise not only promotes safeguarding of sensitive information and infrastructure but also bolsters national security by thwarting potential cyberattacks and maintaining operational resilience.[7] As a response to this contemporary issue, the US National Cybersecurity Strategy Implementation Plan provisions the development of a national strategy to strengthen the cybersecurity expertise with a focus on key infrastructures across all economic sectors.[8]
Henceforth, competent cybersecurity expertise facilitates the creation of robust defense systems, safeguarding vital information assets, adjusting to changing cyber risks, fostering cooperation among stakeholders, and compliance with cybersecurity protocols.
The collaborative innovation ecosystem fosters technological advancements crucial for maintaining military readiness and competitive edge. Nations worldwide are recognizing the imperative of agile and collaborative approaches to defense innovation. Shifts in technological leadership have propelled initiatives like the AUKUS partnership, emphasizing the pivotal role of industry-driven innovation.[9] Moreover, countries such as the US, UK, Germany, Japan, and NATO have established organizations to facilitate civil-military scientific cooperation and develop dual-use technologies, underscoring the importance of collaboration between government, academia, and industry. These collaborative ecosystems extends beyond national borders, with defense primes, small and medium-sized enterprises, and research institutions collaborating on global defense projects. For instance, Australia’s growing defense innovation ecosystem serves as a testament to this collaborative effort, with successful projects like the STRIX Tactical Uncrewed Aerial System[10] demonstrating the effectiveness of defense-industry-academia partnerships. As nations navigate evolving security challenges, the collaborative innovation ecosystem remains a cornerstone of strength for the defense industry, ensuring technological innovation and military preparedness in an increasingly complex geopolitical landscape.
- Strong government support
Strong government support and investment in defense initiatives through allocating larger defense budgets, government contracts, and an emphasis on interstate collaboration provide stability and long-term prospects for growth.
Allocating larger defense budgets by governments to address national security concerns is a consequence stemming from the current war in Ukraine and the escalating conflicts in the Middle East, coupled up with the tensions in the South China Sea. Stockholm International Peace Research Institute-SIPRI highlighted the rise of military expenditures globally, with Europe experiencing a notable uptick due to the Russian-Ukrainian conflict and the next round of the hostilities in Gaza, while Asia and Oceania are propelled by China’s military and economic modernization trends amid escalating regional tensions.[11] Noteworthy mentions with a defense budget increase for 2024 are the Republic of Korea, Taiwan, Japan, and India, to name a few. Interestingly, Türkiye pledged to boost its 2024 defense budget by allocating 150 percent more funds than the previous year. The US on the other hand planned an increase of less than one percent for 2024; however, in comparison to other countries, US is at the forefront, allocating more funds than the next ten countries combined.[12] Therefore, governments around the globe are allocating more funds for defense triggered by the raging conflicts and rising escalating tensions.
Government contracts play a pivotal role in the global defense industry, serving as a major avenue for businesses to contribute to national security efforts and support defense-related initiatives worldwide. These contracts awarded by government entities encompass a diverse range of activities, including research and development, weapons production, infrastructure projects, and cybersecurity initiatives. They also offer a stable revenue stream and provide assurance of long-term business viability and it’s not uncommon for government contracts to comprise anywhere from 50 percent to over 90 percent of a contractor’s total revenue.[13]
However, securing government contracts is a highly competitive and complex process, often requiring adherence to stringent regulatory frameworks and compliance with various standards, exemplified through the regulations of the US DoD.[14] Therefore, strategic engagement with government entities and effective contract management are essential for success in this sector.
Interstate collaboration initiatives underscore a concerted global effort to bolster defense capabilities, foster collaboration, and enhance security on regional and international fronts. The European Union’s adoption of the European Defense Industry Reinforcement through common Procurement Act exemplifies a strategic move to incentivize cooperation among member states, with a focus on common procurement and solidarity.[15] Similarly, Bulgaria’s expressed interest in defense collaboration with Republic of Korea, signals a growing trend of international partnerships aimed at technological exchange and mutual defense enhancement.[16]

In a different occasion, during the Seoul Defense Dialogue 2023, Korean officials stressed the urgent need for international cooperation to address DPR Korea’s advancing nuclear weapon development, emphasizing that failure to act promptly could lead to catastrophic consequences globally.[17] In addition, US DoD is actively pursuing international cooperation in the responsible and ethical development of artificial intelligence and autonomy in the military domain. With initiatives such as the Political Declaration on Responsible Military Use of Artificial Intelligence and Autonomy, launched in February 2023 and endorsed by 51 countries, excluding Russia and China, the Pentagon aims to foster international consensus and guide states in the development, deployment, and utilization of military AI. Meanwhile, Ukraine’s initiatives, including the establishment of the Defense Industries Alliance and plans for a specialized economic regime and defense fund, underscore a proactive approach to international cooperation and export support, with a focus on enhancing defense capabilities and fostering innovation. The same trend can be seen in Germany as well, where the German Chancellor appealed for cooperation among European nations to provide decade-long purchase guarantees for the defense industry. Collectively, these developments reflect a global commitment to leveraging international cooperation as a critical pillar in strengthening defense industries and advancing security agendas.
- Strategic partnerships
Strategic partnerships among major powers present prospects for defense companies to enhance competitiveness and market reach through joint ventures and collaborations, bolstering their position in the global defense market.
Strategic partnerships are essential for defense companies seeking to enhance their global reach, as they provide access to new markets, facilitate technology transfer, and enable collaborative efforts in research, development, and mutual defense agreements. Recent diplomatic moves reflect this trend, as leaders across the globe are actively seeking to enhance partnerships and alliances to strengthen bilateral relations and address regional and global challenges. Turkish President’s visit to Hungary[18] underscores the determination to deepen their strategic partnership, reflecting mutual interests in various fields such as trade, defense, and energy. Similarly, the agreement between Korean and Indonesian presidents[19] signals a commitment to bolster their strategic partnership, aiming to foster cooperation in economic development, technology exchange, and regional security.
Meanwhile, the Saudi-UK partnership[20] is poised for growth across all sectors, reflecting shared goals in areas like trade diversification, defense collaboration, and cultural exchange. In a significant development, the US and India have also solidified their partnership through a series of new defense deals, highlighting their commitment to regional stability and counterterrorism efforts. Additionally, the longstanding strategic partnership between Pakistan and China continues to deepen, particularly in defense interoperability, as evidenced by ongoing cooperation in military exercises and defense equipment procurement. Moreover, Republic of Korea and Qatar have agreed to elevate their relations to a comprehensive strategic partnership, indicating their shared vision for enhanced cooperation in diverse fields including energy, infrastructure, and investment. These partnerships and alliances play a crucial role of international cooperation in addressing complex geopolitical challenges and grant prospects to the defense industry.
02
Weaknesses
02
Weaknesses
The defense industry faces notable weaknesses, characterized by dependence on government contracts, susceptibility to regulatory changes, cyber vulnerabilities, budgetary constraints, and projects’ cost overruns and delays.
- Dependence on government contracts
Dependency on government contracts exposes defense companies to weaknesses associated with budget cuts and changes in political priorities. Dependency on government contracts is particularly evident during rising demands of defense products.[21] On the other hand, since the customer is the government, the price cost is not an issue. However, changes in the political landscape in markets of interest are exposing the weaknesses of the defense industry. Such fluctuations are evident in Korea’s efforts to increase import-export lending to support significant defense sales, amid facing obstacles due to political deadlock preceding the April 2024 parliamentary election, highlighting the importance of overcoming political impediments to sustain defense export ambitions. This reliance can result in financial instability and hinder long-term strategic planning and investment. Additionally, it limits diversification opportunities, leaving companies vulnerable to downturns in defense spending and reducing their ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Regulatory changes
Regulatory changes pose weakness for defense companies seeking to navigate complex compliance landscapes, including new compliance requirements, changes in cybersecurity regulations, as well as changes in export control restrictions.
New compliance requirements introduce regulatory changes, risking legal and financial repercussions for defense firms in case of non-compliance. These changes, arising from government agencies, international bodies, or industry standards organizations, demand continuous monitoring and adaptation. Furthermore, non-compliance can compromise national security efforts, posing additional operational risks and creating weakness to defense industry. The erosion of conventional arms control in Europe, as highlighted by SIPRI,[22] underscores the importance of regulatory compliance in safeguarding regional stability and security.
Changes in cybersecurity regulations present significant threats to the defense industry. These changes may expose vulnerabilities if not promptly implemented, leading to increased cyber threats and breaches. Cybersecurity regulations, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework[23] and CMMC,[24] aim to enhance the cybersecurity posture of organizations within the defense sector. However, their effectiveness depends on timely implementation. Delays in implementing cybersecurity regulations can result in outdated or inadequate security measures, making defense companies vulnerable to exploitation by attackers seeking unauthorized access to sensitive information or critical systems.
Changes in export control regulations impacts defense companies’ ability to conduct international trade and affect supply chain management. SIPRI underscores the gravity of such alterations, particularly through the imposition of security-focused trade restrictions on Russia and Belarus by the EU and a coalition of like-minded actors. These extensive export control restrictions disrupted the flow of parts and components to Russia’s defense industry, highlighting the tangible impact of export control regulations on international trade dynamics within the defense sector. Moreover, despite these restrictions, indications suggest that Russia continued to acquire many of these items from non-participating states, indicating the complex challenges defense companies face in navigating export control restrictions.
Download Report
Defense Industry’s Strategic Outlook – SWOT Analysis
The defense industry must vigilantly assess its strategic position to ensure its readiness to meet the challenges and opportunities of tomorrow.
The heightened geopolitical tensions resulting from the invasion of Ukraine had a notable impact on the operations of the four multilateral export control regimes, including the Australia Group, the Missile Technology Control Regime, the Nuclear Suppliers Group, and the Wassenaar Arrangement. However, the degree and manner of disruption differed among these regimes. While these regimes resumed their activities, the nature and extent of disruption varied, further complicating international trade for defense companies. These disruptions hamper supply chain management efforts, as defense companies should cross evolving regulations and compliance requirements across multiple jurisdictions.[25] In conclusion, changes to export control regulations have the potential to hinder defense companies’ international trade activities and disrupt supply chain management.
- Cyber vulnerabilities
Cyber vulnerabilities expose defense systems and networks to heightened risk of ransomware attacks, while foreign intelligence entities target commercial defense startups, potentially compromising sensitive information, critical infrastructure, national security, and economic interests.
Heightened risk to ransomware and other cyber threats among small and medium-sized defense contractors stems from digital weaknesses, outdated software, and inadequate cybersecurity measures.[26] This is evidenced by the recent spike in malicious cyber activity targeting US government agencies and defense companies, where reports reveal a monthly 18 percent increase in cyberattacks against these entities, with a particular focus on exploiting known vulnerabilities and using malware programs designed to steal information and credentials. This heightened vulnerability is exacerbated by the potential for government shutdowns, as evidenced by concerns raised by analysts regarding the impact on cybersecurity capabilities during such periods.[27] The interconnected nature of the defense sector’s supply chain exacerbates the risk, as breaches in smaller companies provide adversaries with easier access to larger, better-protected contractors.
Foreign intelligence entities also pose a considerable weakness, leveraging sophisticated tactics to infiltrate and exploit critical technologies and intellectual property. These entities target defense contractors and suppliers, aiming to gain access to sensitive information through various means, including cyber espionage, insider recruitment, and strategic partnerships, targeting technology assets and intellectual property of commercial defense startups, thereby jeopardizing national security and economic interests.[28] The theft of proprietary data not only compromises national security but also undermines the competitive advantage of defense companies in the global market. Moreover, such incursions can erode trust in supply chains and disrupt the integrity of defense systems, necessitating robust countermeasures to safeguard against foreign intelligence threats.
In conclusion, cyber vulnerabilities pose a significant weakness to defense systems and networks, increasing the susceptibility to ransomware attacks. Moreover, foreign intelligence entities target emerging commercial defense startups, potentially jeopardizing sensitive information, critical infrastructure, and the broader interests of national security and economic stability.
- Budget constraints
Budget constraints are a weakness of the defense industry that is limiting resource allocation for research, development, further leading to reduced defense spending, impeded modernization efforts, and diminished technological superiority.

Reduced defense spending as a result of changes in governing administrations jeopardizes national security and hampers the ability to adapt to evolving threats, maintain operational effectiveness and sustain technological advancements necessary for maintaining strategic superiority, even though governments around the globe are allocating more funds for defense triggered by the current conflicts in the geopolitical hotspots.[29] This further compromises military readiness, and diminishes technological superiority. For instance, the recent Bank of Brazil’s decision to stop using its own resources to finance defense companies, affected the availability of funds for defense exports in Brazil, and will likely lead to reduced investment in defense projects and capabilities, constraining the industry’s ability to innovate and modernize.
Impeded modernization efforts are also a factor of weakness worth considering. The Ukrainian experience revealed the challenges in allocating funds for defense procurement and modernization, particularly in terms of the timeline for spending and procurement processes.[30] Budget constraints compromise readiness by limiting funding for essential defense areas such as research, development, procurement, and maintenance. This results in challenges in maintaining operational preparedness, as reduced defense spending hampers efforts to invest in crucial equipment and logistical support. Delays in procurement processes further exacerbate the situation, hindering the acquisition of modern technologies necessary for maintaining readiness.
Diminished technological superiority poses a considerable hazard to the defense industry and national security. The US DoD has long relied on its technological edge to maintain military dominance and deter potential adversaries. However, as emerging technologies rapidly evolve and near-peer rivals such as China modernize their military capabilities, the risk of technological parity or even inferiority becomes increasingly palpable.[31] Despite the establishment of defense innovation organizations and partnerships with the private sector, there are obstacles in efficiently identifying, developing, and adopting cutting-edge technologies. The lack of alignment among stakeholders, including government agencies, defense contractors, and research institutions, hampers the smooth transition of technology from concept to deployment. This disjointed approach hinders the military’s ability to capitalize on emerging technologies effectively.
In conclusion, budget constraints are hindering the allocation of resources for research and development, resulting in reduced defense spending, hampered modernization efforts, compromised readiness, and diminished technological superiority.
- Cost overruns and delays
Cost overruns and delays represent significant weaknesses within the defense industry, where technical complexities, mismanagement, and design flaws are undermining profitability and erode investor confidence, highlighting challenges in project management and execution.
Technical complexities and/or mismanagement is another weakness within the defense industry, which increases costs and causes delays, impacting the effectiveness of military programs, straining budgets, and eroding public trust. As evidenced by Boeing’s experience with the KC-46 Air Force tanker contract, which incurred USD 7 billion in overruns on a USD 4.9 billion contract, these overruns occur when actual costs exceed initial estimates, often due to unforeseen technical complexities or mismanagement. Additionally, Northrop Grumman’s recent announcement of a nearly USD 1.6 billion pre-tax charge on the B-21 Raider program, including USD 143 million in cost growth, underscores the detrimental impact of cost overruns on major defense projects.
Design flaws further cause delays in project timelines, such as those experienced by Lockheed Martin and its F-35 program, further exacerbating budgetary pressures and hindering the timely delivery of critical defense capabilities.[32] These weaknesses not only jeopardize the successful execution of defense projects but also raise concerns about accountability, transparency, and efficiency within the defense acquisition process.
Failure to effectively mitigate the impact of cost overruns and delays risks is compromising national defense capabilities and undermines the industry’s ability to fulfill its mission of safeguarding national security interests. Therefore, the prevalence of cost overruns and delays in the defense industry underscores the weaknesses, exacerbated by technical complexities, mismanagement, and design flaws, thereby presenting formidable challenges for government agencies and defense contractors.
03
Opportunities
03
Opportunities
Amidst evolving geopolitical landscapes and increasing security challenges, defense companies are presented with significant opportunities, including access to emerging markets, fostering private-public partnerships, expanding market diversification efforts, enhancing cybersecurity capabilities, and participating in modernization programs to meet evolving defense needs globally.
- Emerging markets
Emerging markets influenced by factors such as growing geopolitical tensions, and establishment of new defense-industrial strategies offer growth opportunities for defense companies to expand market presence and tap into new revenue streams, leveraging increasing demand for military capabilities in regions undergoing rapid geopolitical shifts.
Growing geopolitical tensions in Europe and the Middle East provided the defense companies an option to capitalize from these conflicts, which is evidenced by the rising stocks of major defense players,[33] and led investors to inject over USD 600 million in defense funds. Additionally, the perception of increased geopolitical instability often leads investors to view defense stocks as safe havens, further contributing to their rise.
Despite historical data showing that black swan events like 9/11, Brexit, and the Russia-Ukraine war have had limited impact on U.S. corporate earnings, the Israel-Gaza crisis may affect profits in certain sectors.[34] However, amid these uncertainties, increased defense spending could benefit aerospace, defense, and select industrial sectors, presenting opportunities for growth. Yet, the potential for a prolonged or widespread conflict raises concerns about global trade disruption, reduced demand for overseas travel, and risks of oil embargoes.
How can we help?
Intelligence Solutions
The combination of business, market and strategic intelligence ensures result-driven outcomes for our customers.
Defense and security solutions
Our holistic business approach to the defense and security industry delivers creative solutions tailored to benefit the defense industry stakeholders.
Risk management
Risk management through the responsibility of taking risk ownership while ensuring safety and security
The implementation of new defense-industrial strategies is exemplified through the rise of Republic of Korea’s defense sector, which certainly presents another emerging market for the defense industry. With arms sales soaring to USD 17.3 billion in 2022, the country’s defense sector has capitalized on critical opportunities, particularly in securing major contracts with Central and Eastern European countries like Poland and Bulgaria. The country’s competitive technologies, robust production capacity, and cost-effectiveness position it as an attractive partner for defense procurement,[35] potentially enabling it to consolidate as one of the top five defense industrial centers. Moreover, the EU, recognizing the imperative of aligning defense -industrial initiatives, embarked on formulating the new European Defense Industrial Strategy, aiming to bolster defense capabilities of member states as well as strengthen EU’s role as a geopolitical actor in alignment with the Strategic Compass.
Briefly, emerging markets offer substantial opportunities for the defense industry, fueled by growing geopolitical tensions, and the implementation of new defense-industrial strategies.
- Private-public partnerships
Private-public partnerships (PPPs) present a significant opportunity for the defense industry. Boosting overall defense capabilities through PPPs demonstrates the potential for shared investments and risk mitigation opportunity, influencing the geopolitical dynamics, as seen from the experience from the Ukrainian war. For instance, SpaceX’s provision of cutting-edge satellite communication services to Ukraine during the current conflict in Ukraine[36] demonstrates how these partnerships can leverage corporate innovation with efforts to strengthen national security. Moreover, companies such as Microsoft, Amazon, and Meta have offered cyber defense assistance and combat disinformation campaigns, showcasing the value of PPPs in bolstering cybersecurity defenses.[37] Thus, private-public partnerships offer the defense industry a valuable opportunity to harness corporate expertise, innovation, and economic leverage in support of national security objectives. By collaborating with private corporations, governments can access cutting-edge technologies, bolster cybersecurity defenses, and influence geopolitical dynamics to enhance overall defense capabilities.
- Market diversification

Market diversification reduces reliance on specific regions or product lines, enhancing resilience and long-term growth prospects. Market diversification is a strategic imperative for defense industries seeking to mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities in an evolving global landscape. With geopolitical shifts and increasing volatility, diversifying markets becomes paramount, as evidenced by Turkey’s efforts to expand its defense industry presence in Egypt and other African countries,[38] as well as Qatar’s exploration of advanced military equipment from Germany and Hungary.[39]
Furthermore, partnerships between international defense giants and local companies, such as Lockheed Martin’s collaboration in Saudi Arabia and Korea’s initiatives with Poland, underscore the significance of diversifying market engagements. These efforts not only enhance economic resilience, but also foster technological exchange, bolstering defense capabilities and contributing to regional security dynamics. In an era marked by geopolitical uncertainties and changing market dynamics, market diversification emerges as a critical strategy for defense industries to navigate complexities and sustain growth amidst evolving geopolitical landscapes.
- Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity presents a strategic opportunity for the defense industry to fortify national security by leveraging technological advancements and fostering collaboration between stakeholders. In an era characterized by pervasive cyber threats, cybersecurity emerges as a strategic imperative for the defense industry, offering an opportunity to enhance national security through proactive measures and innovative solutions.
By harnessing technological advancements in cybersecurity, defense contractors can bolster the resilience of critical infrastructure, safeguard sensitive data, and mitigate evolving cyber threats.[40] Moreover, the collaborative efforts between industry, government, and military entities[41] facilitate information sharing, policy advocacy and technological innovation, positioning the defense industry as a key player in safeguarding a nation’s cyber domain. Through strategic investments in cybersecurity capabilities and fostering public-private partnerships, the defense industry not only strengthens its own resilience but also contributes significantly to national security objectives in an increasingly digitalized landscape. In summary, cybersecurity offers the defense industry a strategic opportunity to enhance national security by leveraging technology and fostering collaboration among industry, government, and military stakeholders.
- Modernization Programs
Modernization programs for the defense sector create opportunities for companies to provide innovative solutions and develop cutting-edge capabilities, upgrade existing systems, positioning themselves as key partners in enhancing national security capabilities and differentiate from competitors. Governments, particularly in Europe and Asia, are investing in modernizing their defense capabilities, creating opportunities for companies offering innovative and high-tech solutions. The US defense sector is also undergoing modernization of weapon systems and next-generation capabilities.[42] These advancements, spanning hypersonic missile defense, artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, and swarm drones, present the industry with a unique chance to develop cutting-edge capabilities that can revolutionize military operations. Meanwhile, the Turkish combat aircraft development program has reached its final stages of the development of its first aircraft of the fifth generation, aiming to ultimately replace the F-16 fleet. Noteworthy mention is that the aircraft is locally made, revealing Türkiye’s intentions to join the select group of nations that possess complete control over the entire process of producing advanced combat aircraft, encompassing expertise, infrastructure, skilled personnel, and manufacturing capacity.
Moreover, in Europe, Poland serves as a compelling example which has been actively modernizing its armed forces and investing in defense capabilities to address evolving security challenges.[43] Ukrainian military-industrial sector on the other hand is also experiencing a strategic shift toward prioritizing indigenous arms production and technological innovation, following Türkiye’s example. Besides, by investing in research and development and incorporating state-of-the-art technologies into their products, defense companies can gain a competitive edge in the global market, effectively differentiating themselves from competitors.
In conclusion, government-backed modernization programs in the defense sector present significant opportunities for companies to innovate, develop advanced capabilities, and upgrade systems. By leveraging these investments, defense companies can establish themselves as vital contributors to national security, distinguishing themselves from competitors while enhancing overall defense capabilities.
04
Threats
04
Threats
The defense industry faces significant threats stemming from geopolitical instability, economic uncertainty, and ethical concerns, which must be carefully addressed to mitigate risks and sustain competitiveness.
- Geopolitical Instability
Geopolitical instability poses threats to defense companies hampering international cooperation, impacting market stability, supply chains, and security.
Hampered international cooperation among defense stakeholders occurs particularly in relation to the existence of divergent national interests, imbalance of power and mutual distrust.[44] The ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict, for example, became a stumbling block for allied countries,[45] due to the divergent stances of individual countries on how Ukraine ought to be helped. This situation underscores how regional conflicts hinder collaboration and joint development projects crucial for the defense industry.
Market stability is crucial for defense companies operating in conflict-affected regions, but geopolitical instability poses a significant threat. As conflicts escalate or geopolitical tensions rise, market conditions become unpredictable, affecting the operations and profitability of defense firms in these areas. Geopolitical instability has the potential to undermine financial market stability as they may lead governments to implement financial constraints, restrict cross-border credit, trade, and investment, and instigate capital flight,[46] making it difficult for defense companies to forecast demand and plan production. Sudden escalations in conflict can lead to fluctuations in defense spending and procurement priorities, impacting the revenue streams of defense contractors operating in conflict-affected regions.
Download Report
Defense Industry’s Strategic Outlook – SWOT Analysis
The defense industry must vigilantly assess its strategic position to ensure its readiness to meet the challenges and opportunities of tomorrow.
Disrupted supply chains are another consequence of geopolitical instability, hindering the flow of raw materials, components, and finished products for manufacturing, including defense products. This further disrupts production schedules and increases costs for defense companies operating in such regions, affecting their competitiveness and profitability. For instance, the conflict in the Red Sea has led to disruptions in the global supply chain[47] and heightened security risks, which led to disrupting the global trade.[48] Therefore, geopolitical instability presents a significant threat to defense companies operating in conflict-affected regions, impeding international cooperation, impacting market stability, supply chains, and security.
- Economic Uncertainty
Economic uncertainty triggered by geopolitical instability has the potential to increase inflationary pressures, trade disputes and sanctions ultimately disrupting global supply chains, limit market access, affecting revenue streams and profitability for defense companies.

Inflationary pressures because of geopolitical instability increase the cost of raw materials, labor, and production inputs, leading to higher operating expenses for defense manufacturers. Additionally, inflation erodes purchasing power, reducing the affordability of defense products and services for governments and defense contractors. This subsequently results in delayed procurement decisions and reduced demand for defense goods, affecting the revenue streams and profitability of defense companies.[49] Moreover, inflation can also disrupt financial planning and forecasting, making it challenging for defense companies to accurately predict future costs and revenues, further exacerbating economic uncertainty.
Trade disputes among nations are posing significant threats for defense companies reliant on international trade. Trade disputes can result in tariffs, quotas, and other trade barriers, increasing the cost of importing and exporting defense-related goods and technologies. These disruptions in global trade can lead to supply chain inefficiencies, delays in procurement, and higher operating costs for defense manufacturers, evident from the trade disputes between the United States and China.[50] Furthermore, trade disputes further strain diplomatic relations between countries, potentially impacting defense cooperation agreements and technology transfer arrangements.
Sanctions also pose threats for defense companies operating in conflict-affected regions, exacerbating the already complex landscape of economic uncertainty. Economic sanctions restrict access to key markets, limit technology transfer, and disrupt supply chains, impacting the operations and profitability of defense companies. Additionally, sanctions can lead to increased compliance costs as companies navigate complex regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance with international sanctions regimes. Similarly to trade disputes, sanctions also strain diplomatic relations between countries, creating a volatile global market.
In conclusion, economic uncertainty triggered by inflation, trade disputes, and sanctions presents significant threats for defense companies, impacting their operations, revenue streams, and profitability.
- Ethical Concerns
Ethical concerns present complex challenges within the defense industry, affecting its operations and reputation while raising broader societal concerns. Heightened awareness of ethical considerations, such as human rights violations or civilian casualties, can lead to reputational damage and regulatory challenges for defense companies. From the concerns of human cost of conflicts and adherence to self-imposed constraints to the reliance on contractors, ethical dilemmas shape the industry’s effectiveness and public perception.
The human cost of conflicts and the industry’s role in perpetuating violence is one of the threats burdening the defense industry, besides its contribution to economic growth.[51] The escalating tensions in the Middle East triggered social discontent in weapons procuring countries, as exemplified by CAAT’s revelation of UK companies’ involvement in manufacturing components for the F-35 combat aircraft, drawing attention to the broader implications of UK arms supplies to Israel and the ongoing humanitarian crises in the region, emphasizing the imperative of ethical responsibility in global arms trade.
Adherence to pacifist principles presents ethical dilemmas for the defense industry. This is evident in the case of Japan, where efforts to expand arms exports to bolster security capabilities are scrutinized by the Japanese media highlighting concerns about the country’s historical aversion to promoting conflict.[52]
Reliance on contractors in defense operations underscores the need for transparency and accountability. This is evident from Pentagon’s reliance on contractors, which led to the creation of a so-called “camo economy” by heavy contractor involvement, which raises questions about transparency and accountability in military contracting practices and potential conflicts of interest.[53]
In summary, ethical dilemmas within the defense industry not only impact its operations and reputation but also raise broader social concerns, encompassing issues such as the human cost of conflicts, adherence to self-imposed constraints, and reliance on contractors, ultimately shaping both the industry’s effectiveness and public perception.
05
Recommendations
05
Recommendations
As defense investors maneuver the evolving landscape of the industry, it is crucial to consider the long-term outlook and strategic implications of key SWOT factors.
Investors should capitalize on the industry’s strengths to maximize returns. The increased global demand for defense technologies presents lucrative prospects for investment. Companies at the forefront of technological innovation, particularly in areas such as cyber defense and autonomous systems, are poised to thrive. Additionally, companies with strong government support and established relationships with defense agencies offer stability and continuity of contracts, providing a solid foundation for investment.
To address weaknesses inherent in the defense industry, investors should focus on the need to explore alternative revenue streams, diversification and adaptability. Hedging against dependence on government contracts by investing in companies with diversified revenue streams, can mitigate risks associated with budget constraints and regulatory changes and also enhance their overall resilience. Besides, prioritizing investments in companies with agile and proactive business models capable of adapting to evolving compliance requirements is essential to mitigate regulatory risks and ensure long-term viability. Similarly, by adopting an initiative-taking approach to cybersecurity risk management, defense companies can stay ahead of emerging threats, enhance their cybersecurity resilience, and safeguard their operations and critical assets against cyber threats and breaches.
Opportunities abound for savvy investors willing to explore emerging markets and embrace innovative business models. Investing in regions experiencing rapid economic growth and increasing security concerns can yield substantial returns. Moreover, companies engaged in public-private partnerships and market diversification strategies offer attractive investment prospects, leveraging government funding while capitalizing on private-sector innovation and efficiency.
Overcoming the threats such as geopolitical instability and economic uncertainty requires a prudent approach to risk management. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence on ethical practices and corporate governance standards, avoiding investments in companies with reputational risks or ethical concerns. Additionally, maintaining a long-term investment horizon and resisting short-term fluctuations driven by geopolitical events or economic volatility is paramount. Focusing on companies with resilient business models and sustainable growth prospects can help mitigate the impact of external threats on investment portfolios.
By strategically leveraging strengths, mitigating weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and mitigating threats, investors can navigate the complex and dynamic landscape of the defense industry while positioning themselves for long-term success and resilience in an uncertain global environment.

ARTICLE | 36 PAGES